Thermal Haptics for Fire Simulation :
Radiative and Convective Heat Transfer Model from Fire Dynamics Data
DURATION
2023.05 - Present
2 years 8 months
(ongoing)
KEY WORDS
Safety Training
Real-time Simulation Engineering
Thermal Haptics
My Role
Team Leader
Physics Modeling
System Evaluation
This work present a framework that provides users with thermal haptic feedback through a fire training simulation driven by fire dynamics data. Simulations based on fire dynamics data have great potential to reproduce highly realistic fire scenarios. Previous research has primarily focused on enhancing real-time visual realism, whereas attempts to integrate thermal feedback have been relatively limited. Proposed model incorporates fire dynamics data to approximate real-time convective and radiative heat transfer.
Independent Research
|
2023.05 ~ Present
Outcome
[Paper] Hoseok Jung, Jiyoon Lee, and Hyunimin Kang. 2025. Thermal Haptics for Fire Simulation: Radiative and Convective Heat Transfer Model from Fire Dynamics Data. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR ‘25). (Research demonstration). DOI: [https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMAR-Adjunct68609.2025.00305]
[Fellowship] Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea, 6 million won(≃4.5K $), Meta-verse Fellowship 2023
The importance of realistic fire simulation

Fire Dynamics Data Generation and Pre-processing
Getting environment data and fire simulation data

Fire Dynamics Data-Based Thermal Interaction Model
Convective Heat Transfer
Sample ambient air temperature Tₑₙᵥ at the user’s position from FDS (with temporal interpolation) read skin temperature Tₛₖᵢₙ from a sensor
Compute the convective heat flux via Newton’s law of cooling, q = h (Tₑₙᵥ − Tₛₖᵢₙ)
Update q every frame and feed it to the thermal renderer
Thermal Radiation Transfer
Interpolate the time‑varying radiative power from FDS and uniformly place Lambertian point emitters within the fire region
Cast Monte Carlo rays within the solid angle subtended by the skin receiver (with the haptic device attached)
Convert deposited energy from rays to radiative heat flux at the skin and pass it to the renderer
Thermal Rendering
Sum convective and radiative fluxes to obtain the target thermal stimulus q
Use the Ho & Jones thermal contact model to compute the target display temperature,
given current skin/display temperatures and contact resistanceDrive the thermal display to track this target in real time and deliver the sensation


Adaptive Thermal Interface Across Devices
A unified thermal interaction system that adapts to different devices and user contexts.
By distributing thermal feedback across a console controller and a wrist-worn interface,
the system extends spatial heat perception beyond VR headsets,
enabling consistent multisensory experiences regardless of user familiarity with immersive hardware.
VR Mode Application
When a fire breaks out, the environment becomes filled with dense, choking smoke.
To survive, the player must move while crouching.
As a gamification element, remaining uncrouched and exposed to the smoke for a certain duration causes the player’s health to gradually decrease.
If the player’s health is fully depleted, the player fails to escape.
Console Mode Application
User Experience
Through user experiments, it was demonstrated that the rendering algorithm currently applied improves the overall user experience in situations where discontinuous changes in heat flux are need compared to conventional methods
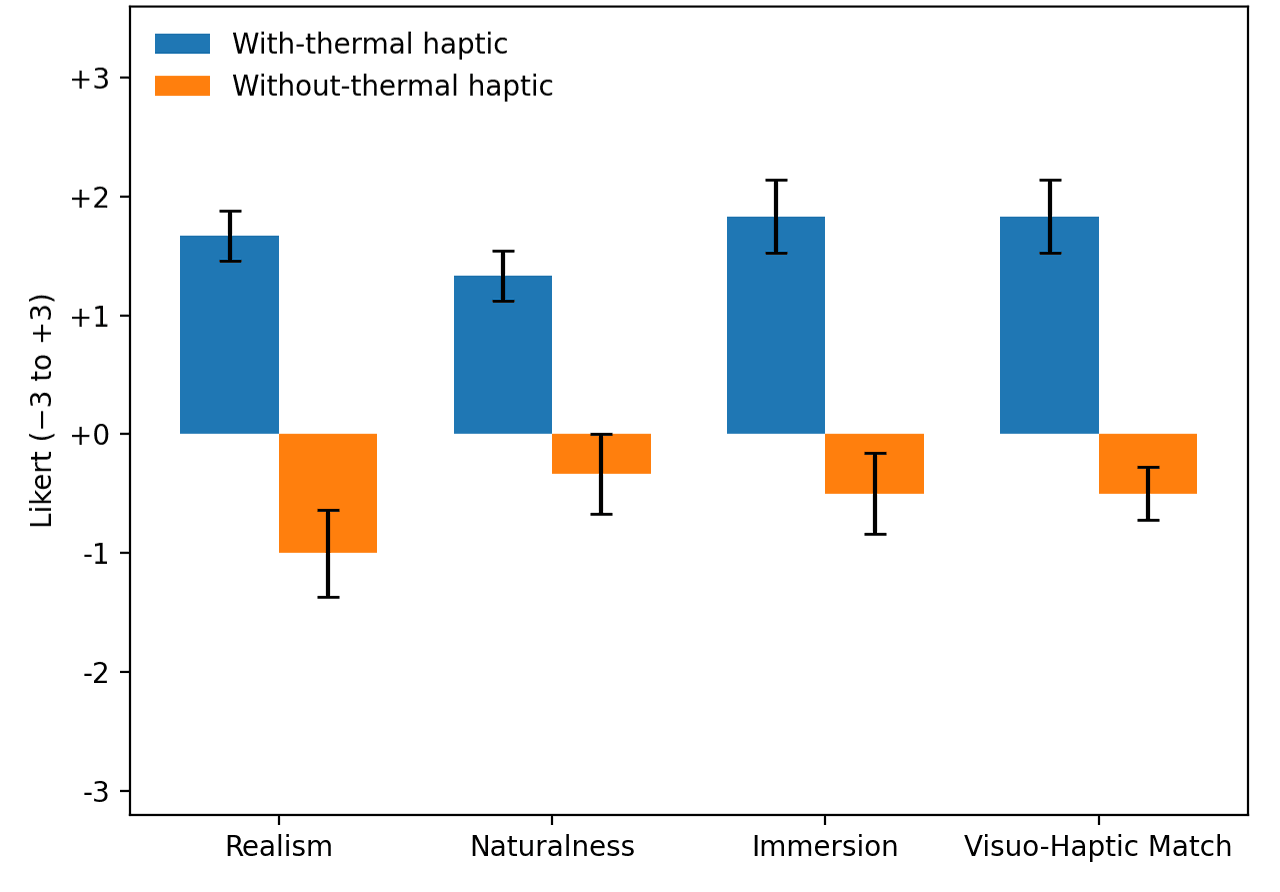
Conclusion
This study proposes a framework that utilizes fire dynamics data to develop a real-time fire simulator and provide corresponding thermal haptic feedback. We introduced an approximation model that calculates the effects of thermal convection and radiation on the user during a fire, optimized for real-time simulation performance. Furthermore, we developed specialized thermal haptic devices tailored for two distinct experimental settings: a console environment and a virtual environment. The proposed framework is expected to enhance the immersion and effectiveness of fire evacuation training, thereby contributing to the establishment of a more systematic and safe educational system.
Role and Responsibility