Tele-sense
DURATION
2023.09 ~ Present
2 years 4 months
(ongoing)
KEY WORDS
HRI
Telehpatic
RESEARCH
Thelehaptic
Contribution
Team Leader
Engineering
Design Research
CO-WORKER
Jiyoon Lee
Sungmo Lee
Seungwon Hu
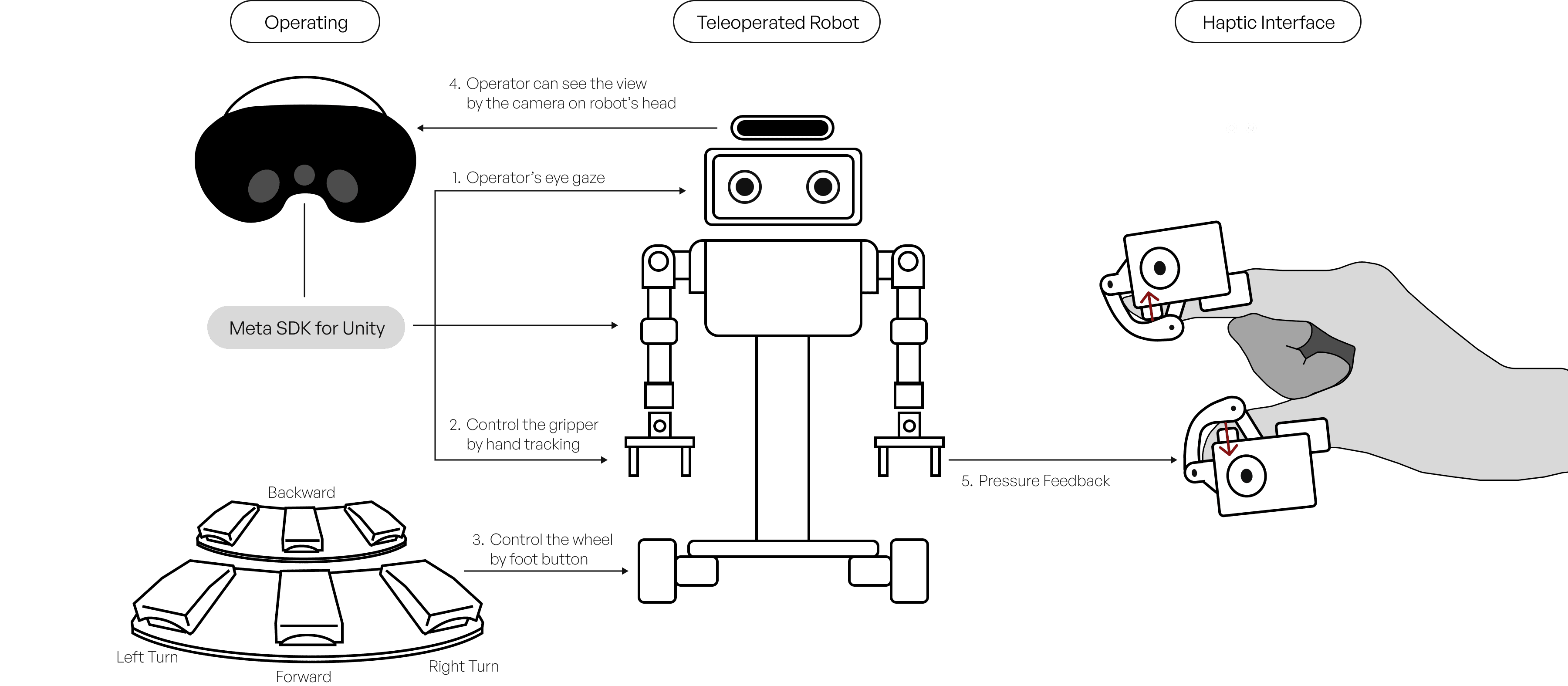
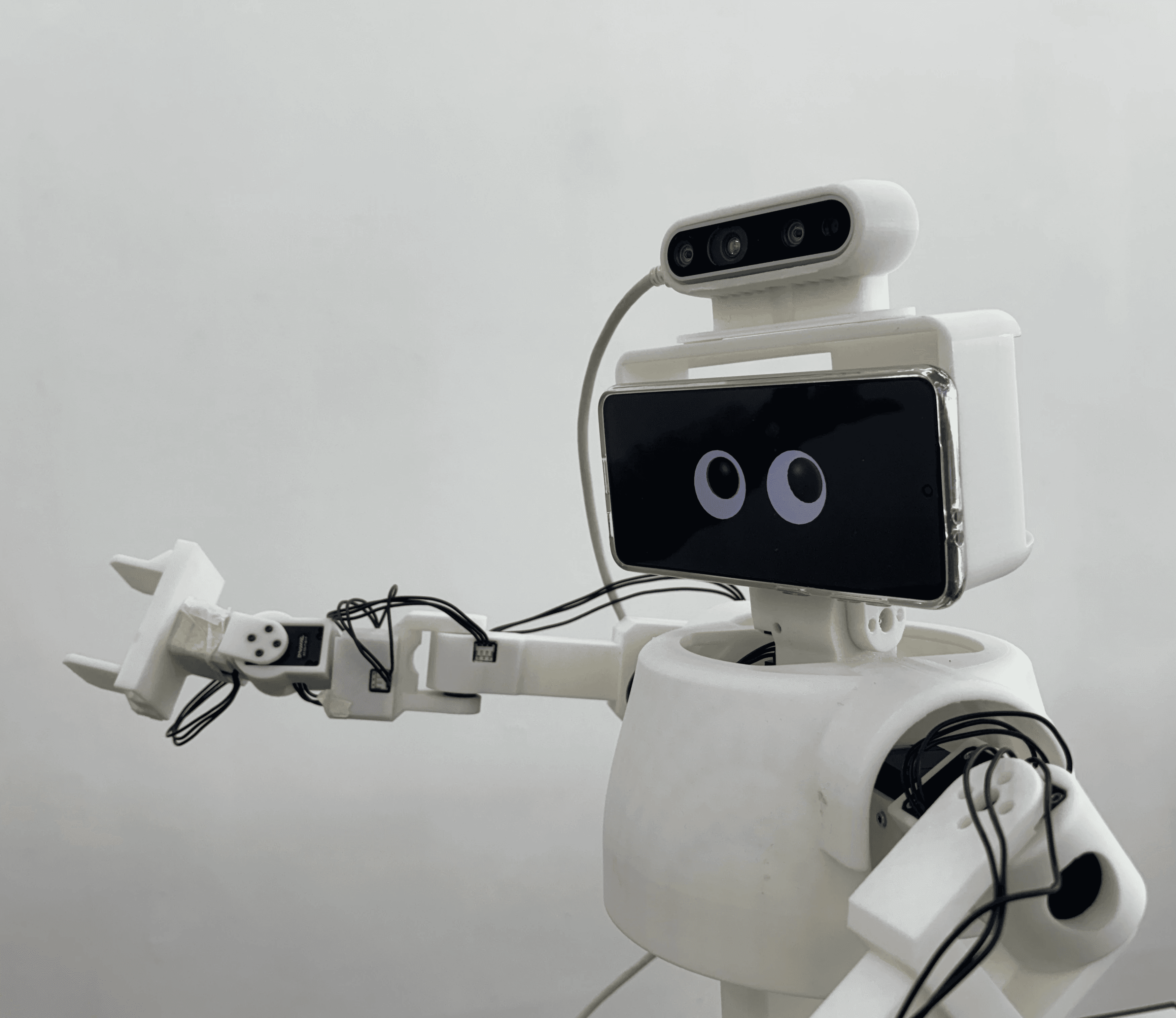
Tele-operated avatar robots serve as a physical extension of the operator, facilitating active and meaningful communication with local users. Recognizing that non-verbal cues are critical for shaping user experience, our system is engineered to deliver rich expressive behaviors. It integrates HMD-based eye tracking to map the operator’s dynamic gaze in real-time, a tele-haptics interface specialized for social touch, and an AI-driven voice modulation system to maintain a consistent character persona. By synchronizing these multimodal signals, the system significantly enhances the naturalness of the interaction, thereby increasing user immersion and engagement.
Indendent Research
|
2023.09 - Present
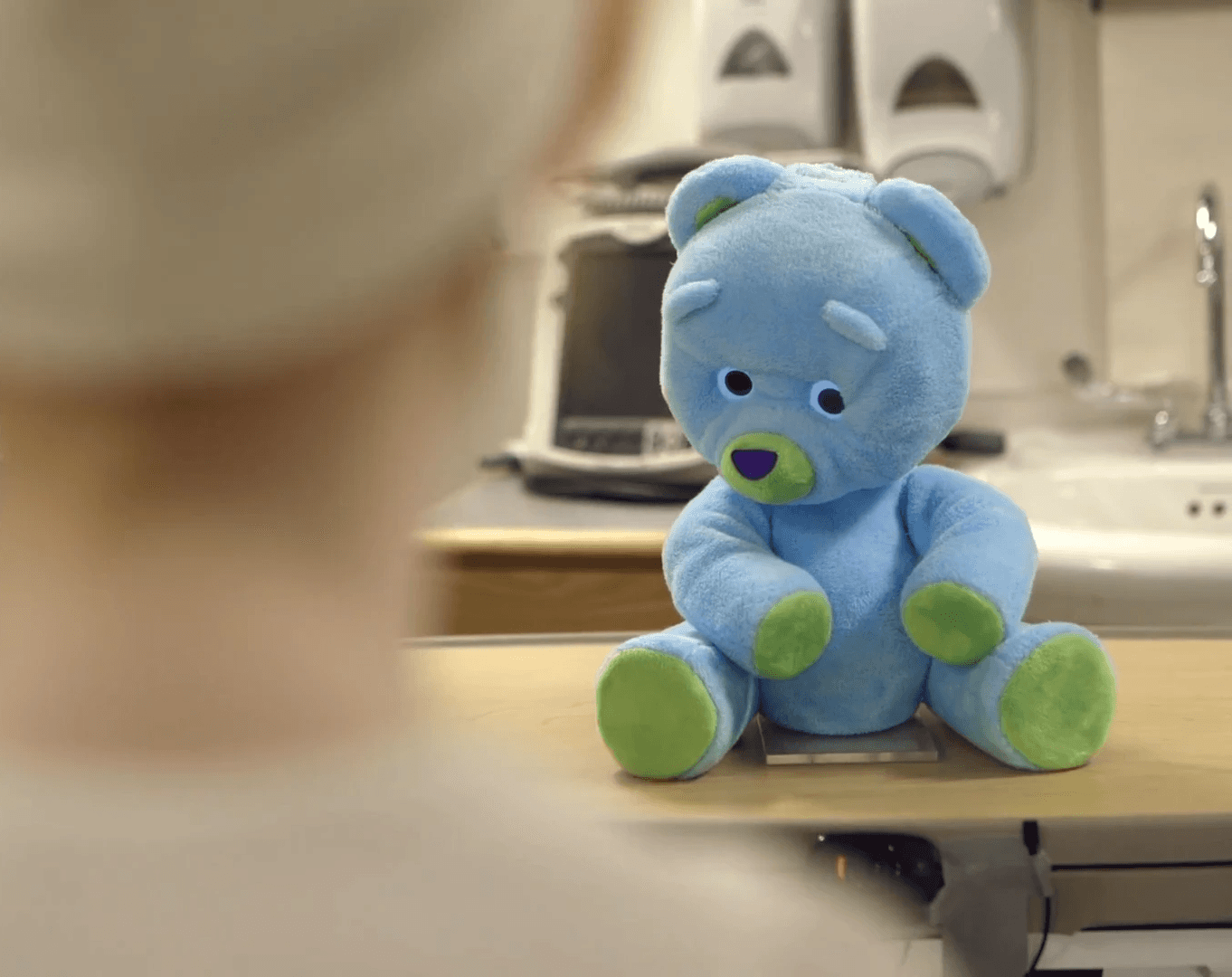


Background
With the increasing adoption of robotic
technologies in healthcare, interest has grown in leveraging robots to support pediatric patients
through rehabilitation and emotional interaction.


Problem
However, most existing teleoperated robots remain focused on simple, conversation-based interactions, with limited research on more complex tasks such as grasping or object handover.

Solution
This project aims to develop a tele-haptic robot system that enables rich and diverse remote interactions between medical professionals and pediatric patients.

Key Interaction
Improve Nonverbal Communication

Paralinguistic
Voice Expression

Eye Gaze
Interaction

Embodied
Gesture Movement

Tele-haptic
Social Touch
User Experience
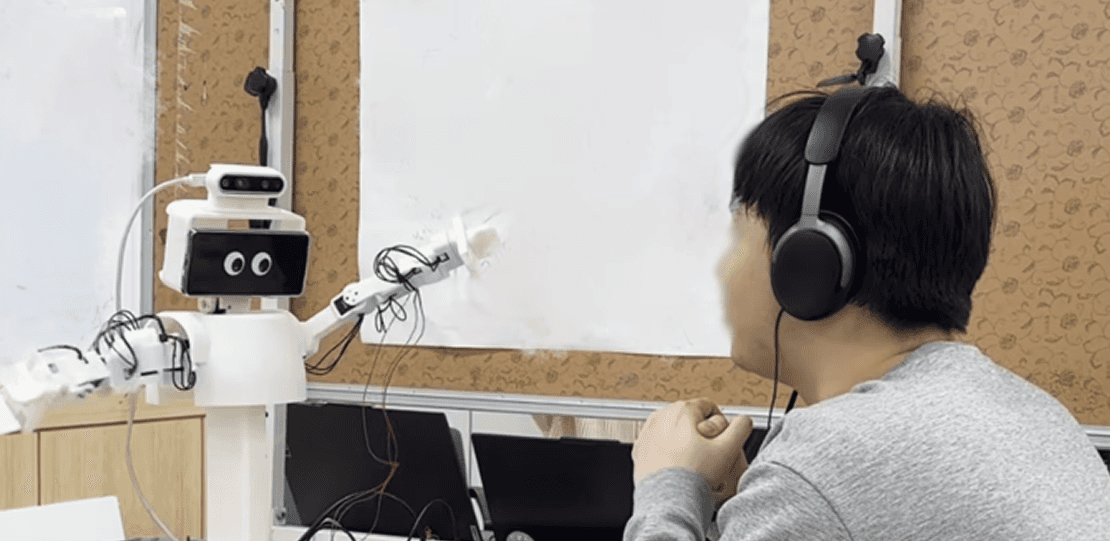

Paralinguistic Voice Expression
In interactions with a teleoperated robot, we considered that users are not engaging with a human operator, but with a robot character.
Therefore, the operator’s voice is not transmitted as-is; instead, it is transformed to create the experience of the robot character speaking directly.
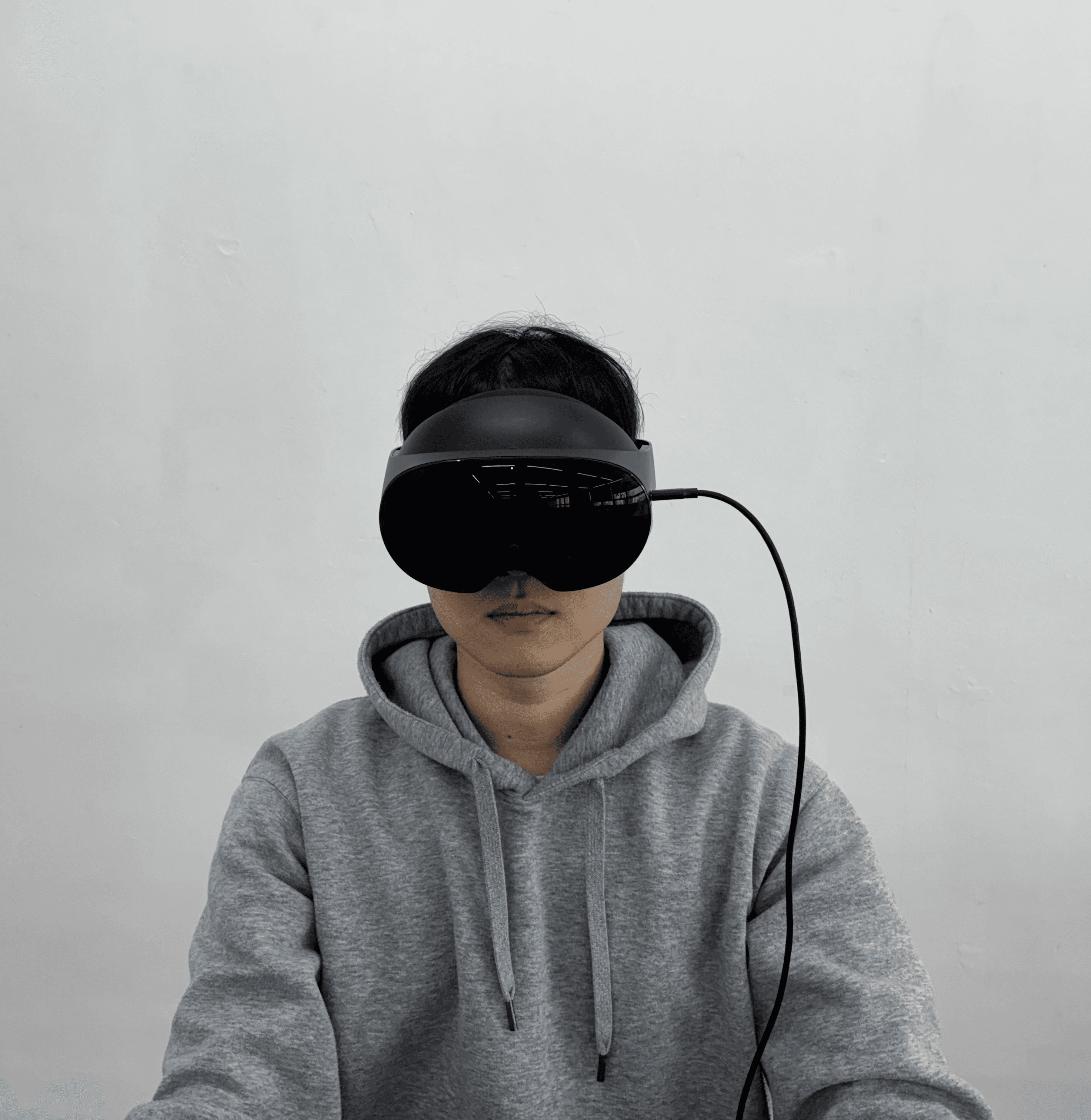

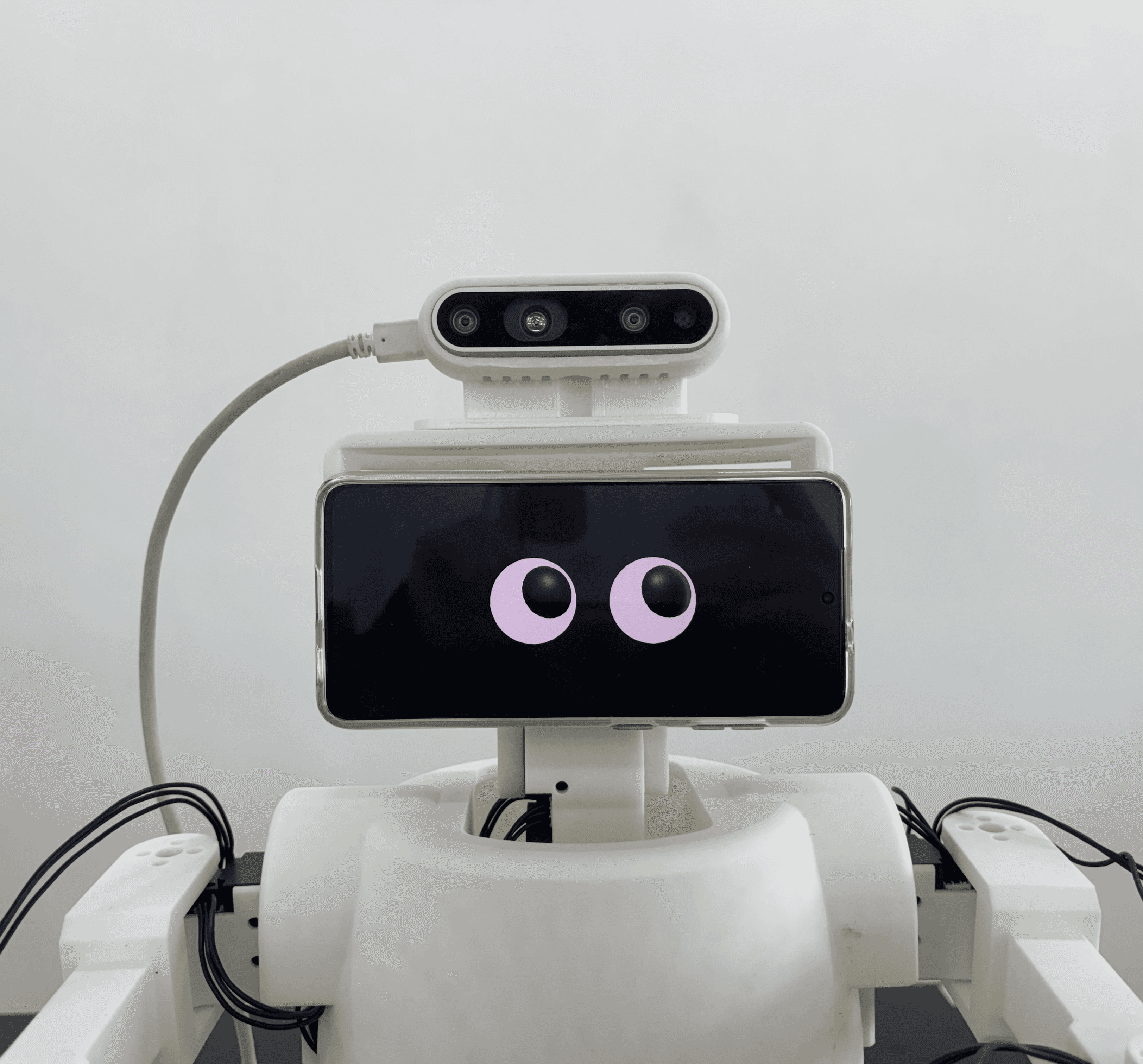
Eye Gaze Interaction
The remote operator’s gaze was directly mapped onto the robot’s eyes.
As a result, the robot’s eye movements reflect the operator’s real-time visual attention, enabling natural and expressive non-verbal interaction.
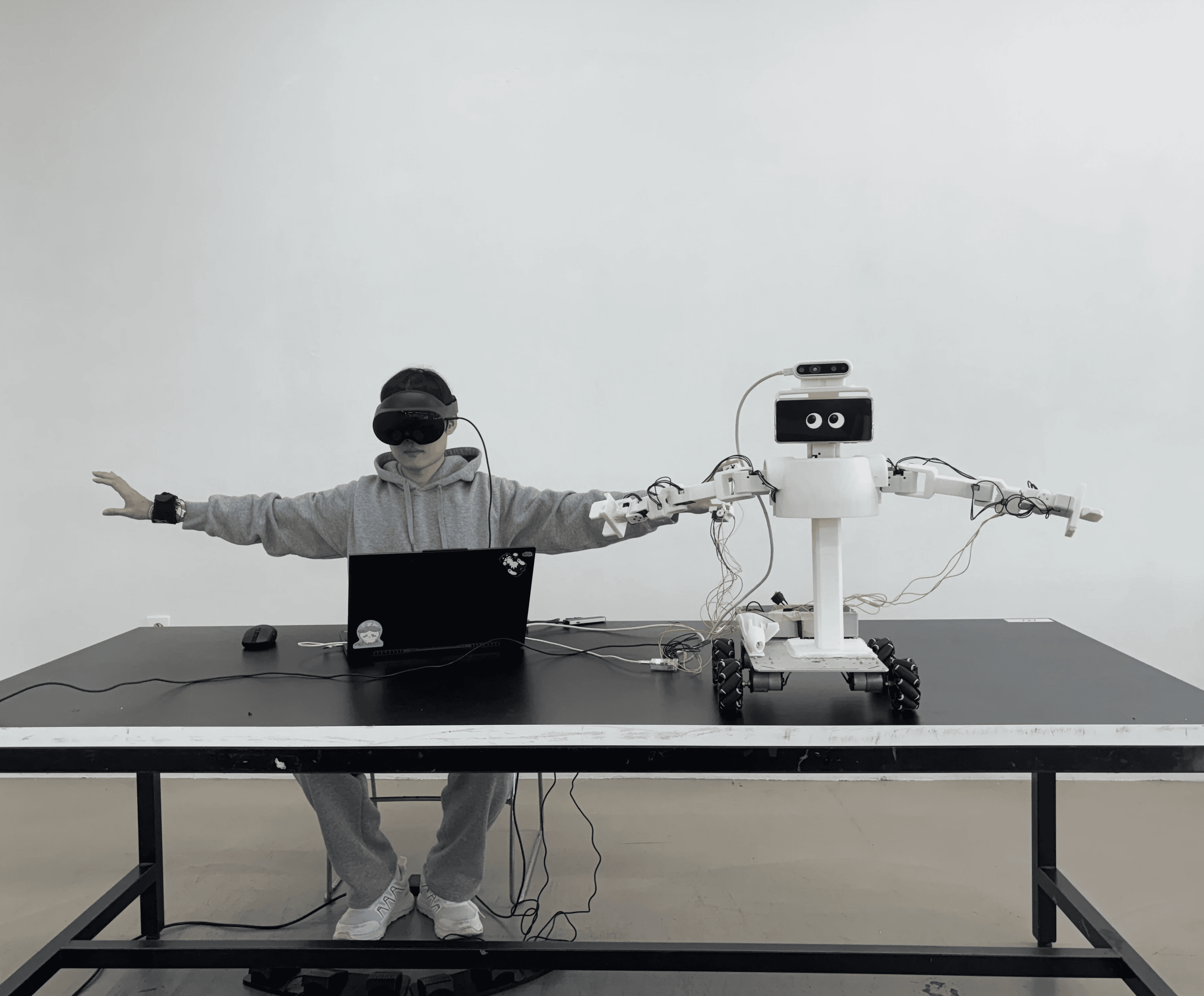
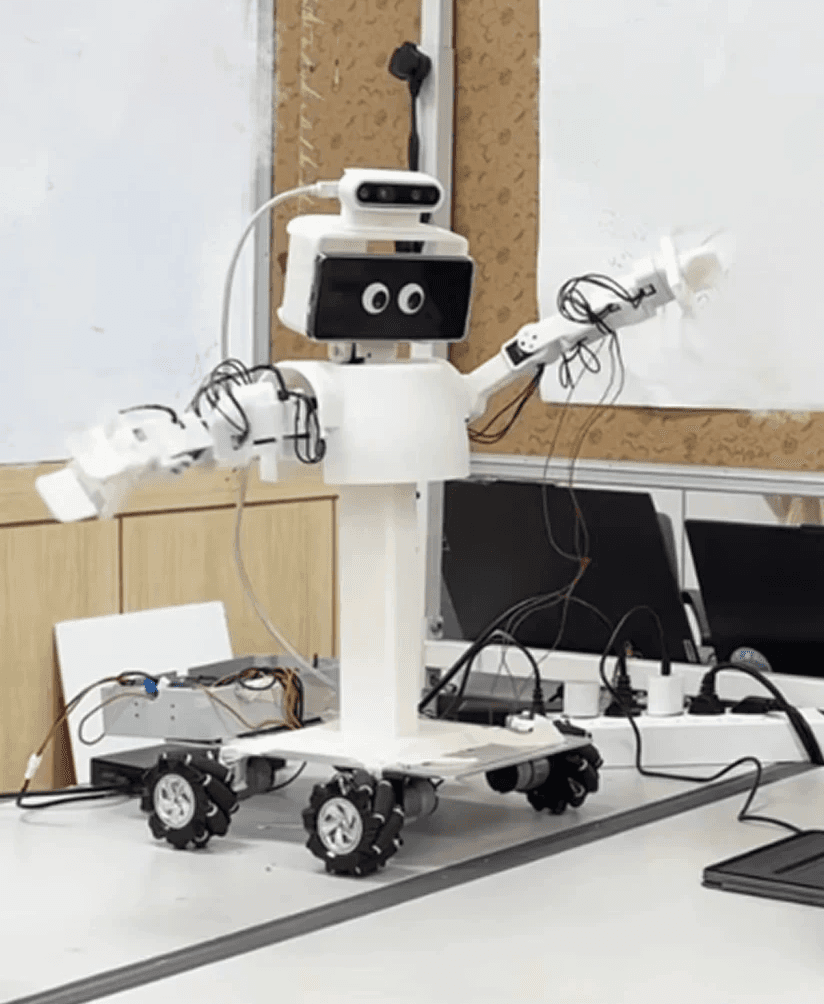
Embodied Gesture Movement
The robot’s upper-body movements are controlled through the user’s physical motions, using inverse kinematics and hand tracking.
Both the neck and arms are mapped to the user’s movements, allowing the robot to mirror the operator’s upper-body behavior in real time.
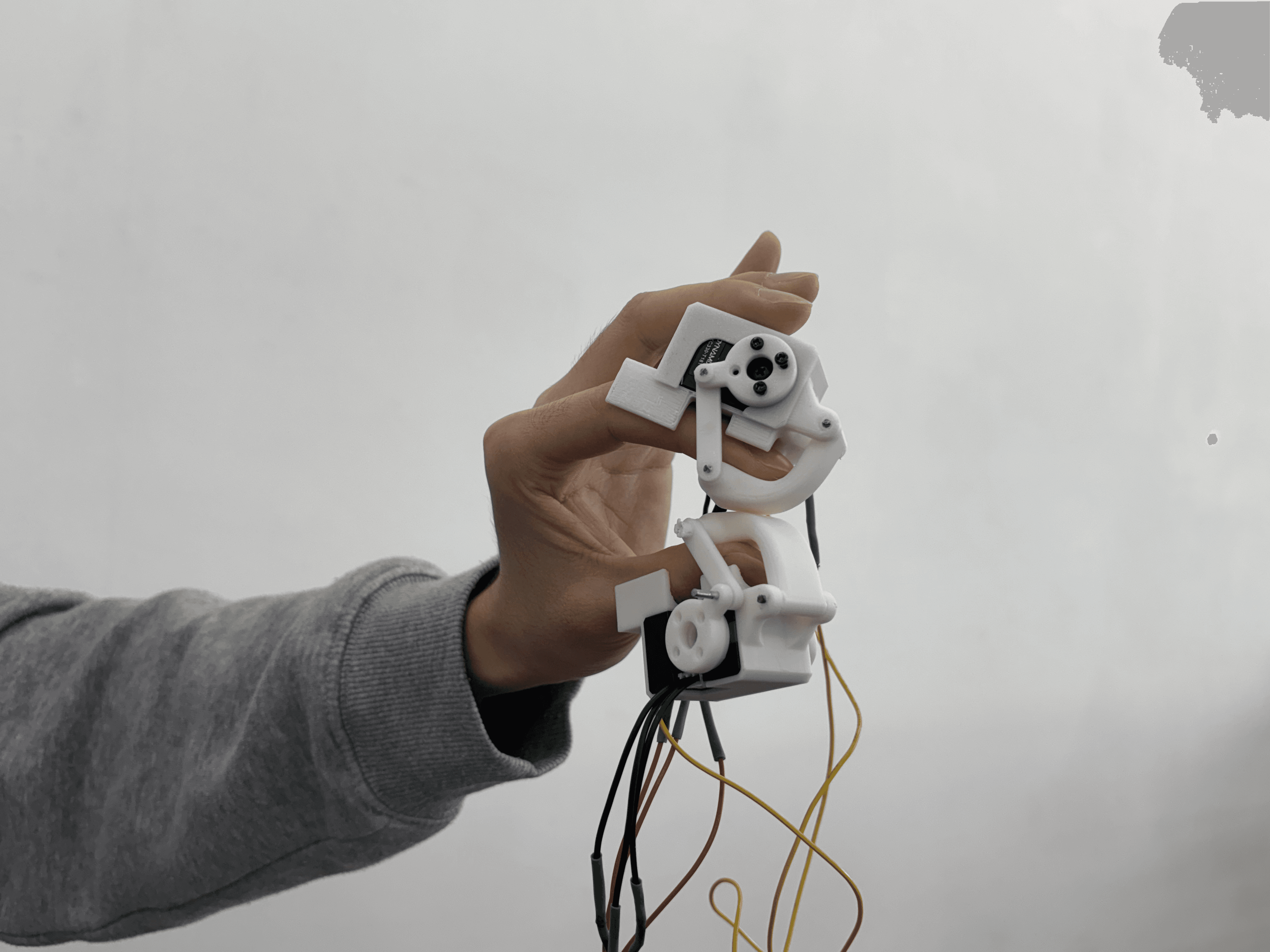
Tele-haptic Social Touch
A haptic interface is used to enable social touch during interaction.
To ensure safety and precision when engaging with a user face-to-face through the robot, torque generated
while grasping objects with the gripper is fed back to the operator as pressure-based haptic feedback.
User Scenario